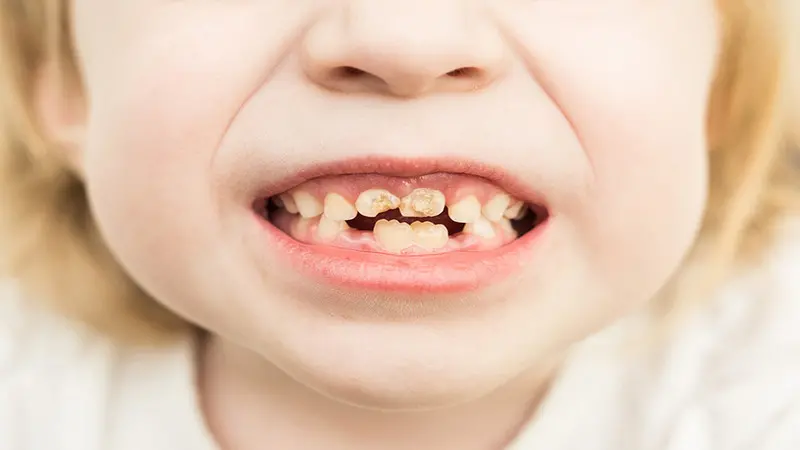
Childhood cavities, also known as dental caries or tooth decay, are a prevalent oral health problem among children worldwide. Tooth decay not only affects a child’s oral health but also their overall well-being and quality of life. Preventing childhood cavities requires understanding the common causes that contribute to their development.
This article will delve into the various factors that contribute to tooth decay in children, providing parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals with valuable insights to help prevent this dental concern.
Poor Oral Hygiene causes cavities in children
One of the primary causes of childhood cavities is inadequate oral hygiene practices. Failure to brush teeth regularly and effectively, as well as not flossing, can lead to the accumulation of dental plaque. Plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, produces acids that attack tooth enamel, leading to decay.

High Sugar Consumption
Excessive sugar consumption plays a significant role in the development of tooth decay in children. Consuming sugary foods and drinks, such as candies, soda, fruit juices, and sweets, provides a food source for bacteria in the mouth, promoting plaque formation and acid production. Frequent and prolonged exposure to sugary substances increases the risk of cavities.

Bottle Feeding and Nighttime Bottle Use
Prolonged bottle feeding, especially at night, is a common cause of tooth decay in infants and toddlers. When babies fall asleep with a bottle containing milk, formula, or juice, the liquid pools around their teeth, leading to the prolonged exposure of tooth surfaces to sugars. This can result in the development of cavities, commonly referred to as “baby bottle tooth decay.”
Lack of Fluoride causes cavities in children
Fluoride is an essential mineral that helps prevent tooth decay by strengthening tooth enamel and making it more resistant to acid attacks. Insufficient exposure to fluoride can increase a child’s susceptibility to cavities. Factors contributing to this include using non-fluoridated toothpaste, consuming non-fluoridated water, or living in areas without fluoridated community water supplies.
Irregular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are crucial for maintaining good oral health and preventing cavities. However, many children do not receive routine dental care, leading to undiagnosed oral health problems, including tooth decay. Lack of dental visits prevents early detection and intervention, allowing cavities to progress and cause further damage.
Inadequate Nutrition
Poor nutrition, particularly deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, can increase the risk of childhood cavities. A diet lacking in nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin C can weaken tooth enamel and impair oral health, making children more susceptible to decay.
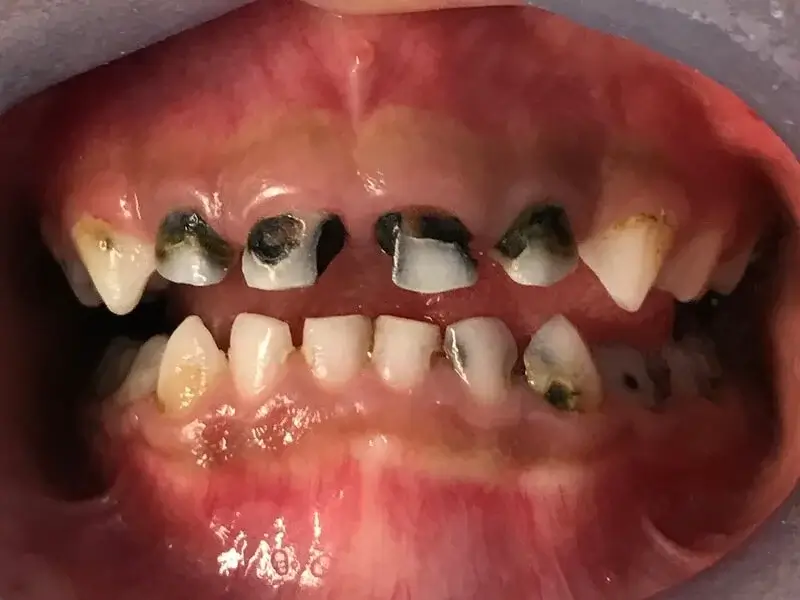
Oral Microbiome Imbalance causes tooth decay in children
The oral microbiome consists of a diverse community of bacteria and other microorganisms that naturally reside in the mouth. Imbalances in the oral microbiome, such as an overgrowth of cavity-causing bacteria like Streptococcus mutans, can contribute to tooth decay in children. Factors like poor oral hygiene, sugary diets, and certain medications can disrupt the balance of oral bacteria, promoting cavity development.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics can also influence a child’s susceptibility to cavities. Certain genetic variations affect the composition and strength of tooth enamel, making some individuals more prone to tooth decay. Understanding the genetic factors involved can help identify high-risk individuals and tailor preventive strategies accordingly.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors, such as low family income and limited access to dental care, can contribute to the development of childhood cavities. Children from disadvantaged backgrounds may have limited access to preventive dental services, fluoride treatments, and education on oral health practices, increasing their vulnerability to tooth decay.
Preventing childhood cavities requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the common causes of tooth decay in children. Encouraging good oral hygiene practices, limiting sugar consumption, promoting regular dental check-ups, and ensuring adequate exposure to fluoride are essential preventive measures. Educating parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals about the causes and prevention of childhood cavities can significantly contribute to improving the oral health of children and reducing the burden of dental caries in the population. By implementing these preventive strategies, we can work towards a future where childhood cavities become a rare occurrence rather than a widespread problem.
(Disclaimer: The information given here is based on general information. Before adopting it, definitely take medical advice. THE MONK does not endorse it.)