It is quite possible that you may not have heard much about the benefits of Vitamin B12, but our body needs it regularly. Let us know the importance of this nutrient and the list of food items related to it.
Vitamin B12 benefits
Vitamin B12 is a very important nutrient that fulfills many needs of our body, because it has an important role in operating important body functions in a better way. We should never lack this nutrient in our daily diet, otherwise serious consequences can come to the fore. Let us tell you why Vitamin B12 is necessary for the body and what foods you have to eat to fulfill it.

Why is Vitamin B12 important?
Making blood in the body
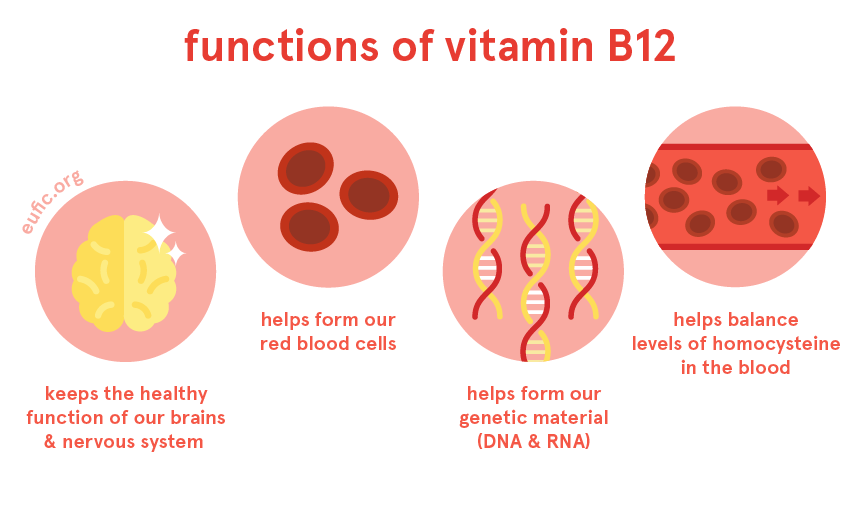
Vitamin B12 plays an important role in the formation of blood cells. It is helpful in the production of hemoglobin (protein that transports oxygen in the blood) and prevents diseases like anemia, this is the disease due to which there is a lack of blood in the body, due to which the person becomes weak and then that daily Cannot do normal activities of life.
Neurological Function
We all know that we cannot do any work without the brake signal, it transmits signals to all parts of the body through neurons. Vitamin B12 plays an important role in the health, development and function of neurons. It is also essential for neuronal myelination (the sheath that surrounds neurons), which helps neurons conduct.
Prevents from these diseases
Vitamin B12 not only helps in body function, but also protects us from many diseases, especially dementia, mental problems, diabetes, skin problems and hair fall. For this, you must eat foods rich in B12.
Absorption and storage
Vitamin B12 requires a protein called intrinsic factor, which is produced in the stomach, for absorption in the small intestine. Moreover, after absorption, vitamin B12 is bound to a protein called transcobalamin and stored in the liver for future use.
Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency can occur due to various reasons, such as inadequate dietary intake (especially in strict vegans and vegetarians), impaired absorption (e.g., due to pernicious anemia or gastrointestinal disorders), or certain medications that interfere with absorption. Moreover, symptoms of deficiency may include fatigue, weakness, tingling or numbness in the hands and feet, difficulty walking, memory problems, and mood changes.
Health benefits of vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is essential for the formation of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. It also helps maintain the health of nerve cells and plays a role in DNA synthesis. Adequate levels of vitamin B12 are important for overall brain function, energy production, and the metabolism of fats and proteins.
Recommended intake
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for vitamin B12 varies depending on age, gender, and life stage. For adults, the RDA is generally around 2.4 micrograms per day. However, individual needs may vary, and it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Supplements
If you have a vitamin B12 deficiency or follow a strict vegan or vegetarian diet, your healthcare provider may recommend a vitamin B12 supplement. However, these supplements come in various forms, including tablets, capsules, sublingual (under the tongue) tablets, and injections. It’s also important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of supplementation.
It’s worth noting that excessive vitamin B12 intake from supplements or fortified foods is generally not harmful because excess amounts are excreted through urine. However, if you have underlying medical conditions or are taking certain medications, it’s always best to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplements.

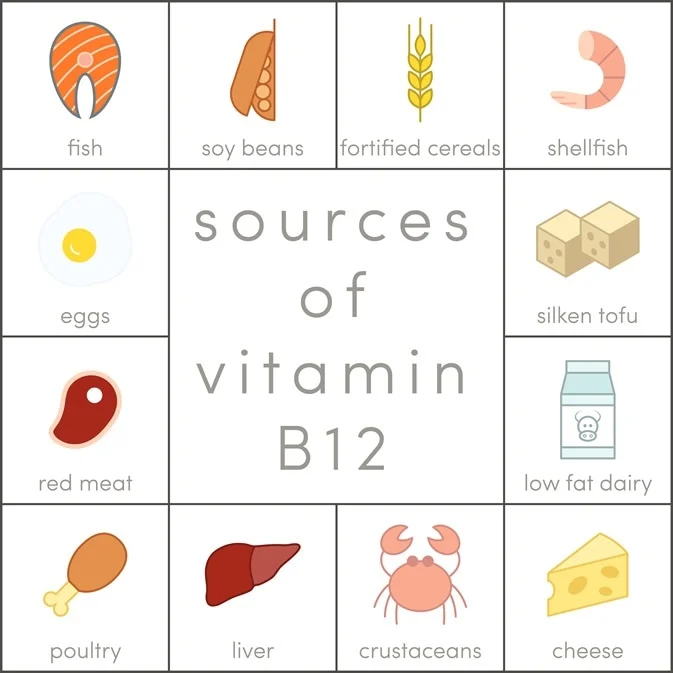
Sources of Vitamin B12 and benefits
- Meat
- Fish (mackerel, salmon, trout, sardines, tuna)
- Lobster
- Milk Products (Milk, Curd, Cheese)
- Eggs
- Fish Oil
- Soybean
- Rice Cakes
- Ghee
- Bread
- Fruit juice
- Makhana
- Coffee Grounds
- Yeast Bread
- Oatmeal
(Disclaimer: The information given here is based on general information. Before adopting it, definitely take medical advice. THE MONK does not endorse it.)