Boosting metabolism and to enhance weight loss is the two sides of the same coin. The relationship between metabolism and weight loss is a topic of significant interest and discussion in the field of nutrition and fitness. Metabolism refers to the complex biochemical processes in your body that convert food into energy. A higher metabolism can aid in weight loss by burning more calories, even at rest. In this comprehensive essay, we will explore the connection between metabolism and weight loss and delve into the foods and dietary strategies that can help increase metabolism and support effective weight loss.
Metabolism is often described in terms of two key components:
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): BMR is the energy expended by your body at rest to maintain basic physiological functions, such as breathing, circulating blood, and regulating body temperature. It accounts for the majority of your daily calorie expenditure, typically around 60-75%.
- Physical Activity and Thermic Effect of Food (TEF): These components of metabolism encompass the energy expended during physical activity and the digestion and absorption of food. Physical activity can significantly increase daily calorie expenditure, while TEF accounts for the calories burned during the digestion and metabolism of food.
In essence, your metabolism determines how many calories your body burns each day. Increasing metabolism can help you create a calorie deficit, which is crucial for weight loss, as you need to burn more calories than you consume.
Factors Influencing Metabolism
Several factors influence an individual’s metabolism:
- Age: Metabolism tends to slow down with age, primarily due to a decrease in muscle mass.
- Body Composition: Muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue. Therefore, individuals with a higher proportion of muscle tend to have a higher metabolism.
- Gender: On average, men have a higher BMR than women because they tend to have more muscle mass.
- Hormones: Hormones play a significant role in metabolism. Conditions like hypothyroidism can slow metabolism, while hyperthyroidism can increase it.
- Diet: The type and amount of food you consume can influence metabolism. For example, the thermic effect of protein is higher than that of carbohydrates or fats.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise, especially strength training, can increase muscle mass and boost metabolism.
- Genetics: Genetics also play a role in metabolism. Some individuals may have naturally faster or slower metabolic rates.
Foods which helps in boosting Metabolism
While genetics and age play a role in determining your metabolism, you can make dietary choices that support a healthy and efficient metabolism. Here are foods that can help boost your metabolism:
1. Protein-Rich Foods
Protein has the highest thermic effect of all macronutrients, meaning it requires more energy to digest and metabolize. This can temporarily increase your metabolic rate. Protein also helps in muscle repair and growth, contributing to a higher BMR over time. Foods rich in protein include:
- Lean meats (chicken, turkey, lean cuts of beef or pork)
- Fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel)
- Eggs
- Dairy products (Greek yogurt, cottage cheese)
- Plant-based sources (tofu, tempeh, legumes, nuts, seeds)

2. Spicy Foods
Certain compounds found in spicy foods, such as capsaicin in chili peppers, can temporarily boost metabolism by increasing body temperature and heart rate. Incorporating moderate amounts of spicy foods into your diet can help rev up your metabolism.

3. Green Tea
Green tea contains catechins, which are antioxidants that have been shown to increase metabolism and promote fat oxidation. Drinking green tea regularly may have a modest effect on weight loss and metabolism.

4. Coffee
Caffeine, found in coffee, is a natural stimulant that can temporarily increase metabolism and energy expenditure. However, its effects can vary from person to person, and excessive caffeine intake is not recommended.

5. Water
Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and can support metabolic processes. Drinking water can also temporarily increase calorie expenditure due to the energy required to process and absorb fluids.

6. Fiber-Rich Foods
Fiber-rich foods, especially soluble fiber, can slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. This can help regulate appetite and potentially support weight management. Foods high in fiber include:
- Whole grains (oats, quinoa, brown rice)
- Fruits (apples, berries, pears)
- Vegetables (broccoli, spinach, carrots)
- Legumes (beans, lentils)

7. Iron-Rich Foods
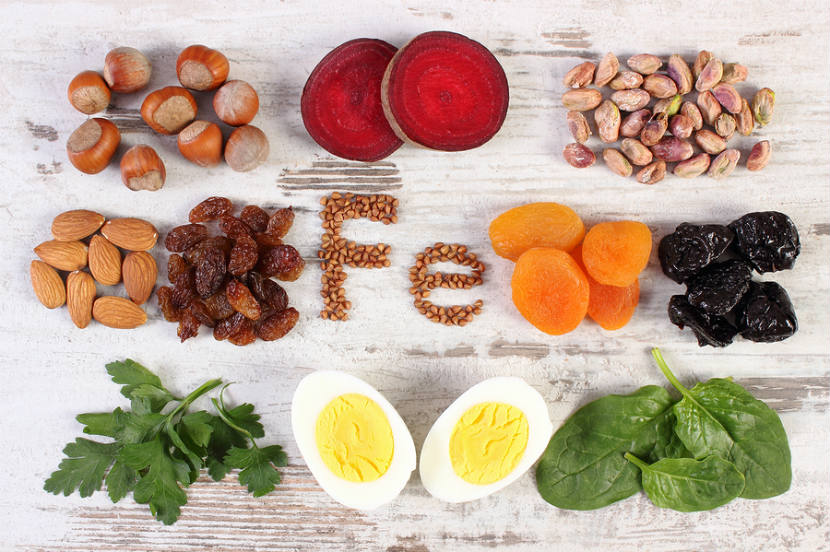
Iron is essential for the production of hemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen in the blood. Adequate iron levels support healthy metabolism and energy production. Good sources of iron include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, and fortified cereals.

8. Foods Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and flaxseeds, can help reduce inflammation and support metabolic health. They may also have a positive impact on insulin sensitivity.

9. Dairy Products
Dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese are rich in calcium and vitamin D. These nutrients are involved in the regulation of metabolic health and can promote the breakdown of fat cells.

Dietary Strategies for Weight Loss and Metabolism Boost
In addition to incorporating metabolism-boosting foods, several dietary strategies can support weight loss and enhance metabolic efficiency:
1. Balanced Diet
A balanced diet that includes a variety of foods from all food groups provides essential nutrients and supports overall health. Aim to consume adequate protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.

2. Portion Control
Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating. Using smaller plates, measuring portions, and paying attention to hunger and fullness cues can help you control calorie intake.
3. Frequent Meals
Some individuals find that eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day helps regulate appetite and prevents excessive calorie consumption. However, meal frequency is a matter of personal preference.
4. Avoid Highly Processed Foods
Highly processed foods are often high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and empty calories. They can lead to weight gain and metabolic issues. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible.
5. Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water is essential for metabolic processes. Sometimes, thirst can be mistaken for hunger, leading to unnecessary calorie intake. Make sure to stay hydrated throughout the day.
6. Include Strength Training
Incorporating strength training exercises into your fitness routine can help build and maintain lean muscle mass. Muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue, contributing to a higher BMR.
7. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can affect metabolism and lead to unhealthy eating habits. Engage in stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to manage stress effectively.
8. Get Adequate Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for metabolic health and overall well-being. Aim for 7-9 hours of restorative sleep per night to support healthy metabolism.

Myths and Misconceptions
In the quest to boost metabolism and lose weight, it’s important to be aware of common myths
and misconceptions:
1. Metabolism-Boosting Foods Alone Lead to Significant Weight Loss
While certain foods can temporarily increase metabolism, significant weight loss requires a combination of factors, including a calorie deficit through diet and physical activity.
2. Eating Spicy Foods Leads to Substantial Weight Loss
Spicy foods can have a modest impact on metabolism, but they are not a magic solution for weight loss. A balanced diet and overall lifestyle play a more significant role.
3. Skipping Meals Boosts Metabolism
Skipping meals can actually slow down metabolism as the body goes into conservation mode, storing energy as fat. Regular, balanced meals are essential for a healthy metabolism.
4. Drinking Ice-Cold Water Burns More Calories
While it’s true that your body burns some extra calories to warm up cold water to body temperature, the effect is minimal and not a substantial contributor to weight loss.
5. The Metabolic Rate Cannot Change
Metabolism is not fixed and can be influenced by various factors, including diet, physical activity, and lifestyle choices. It can be increased to some extent through these strategies.
Metabolism plays a crucial role in weight management, and dietary choices can influence its efficiency. While certain foods and dietary strategies can temporarily boost metabolism, they should be part of a comprehensive approach to weight loss and overall health. A balanced diet, regular physical activity, portion control, and a focus on long-term sustainable habits are key to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. Remember that individual metabolism varies, and what works for one person may not work for another. Consulting with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance for achieving your weight loss and metabolic goals while ensuring your nutritional needs are met.
(Disclaimer: The information given here is based on general information. Before adopting it, definitely take medical advice. THE MONK does not confirm this.)