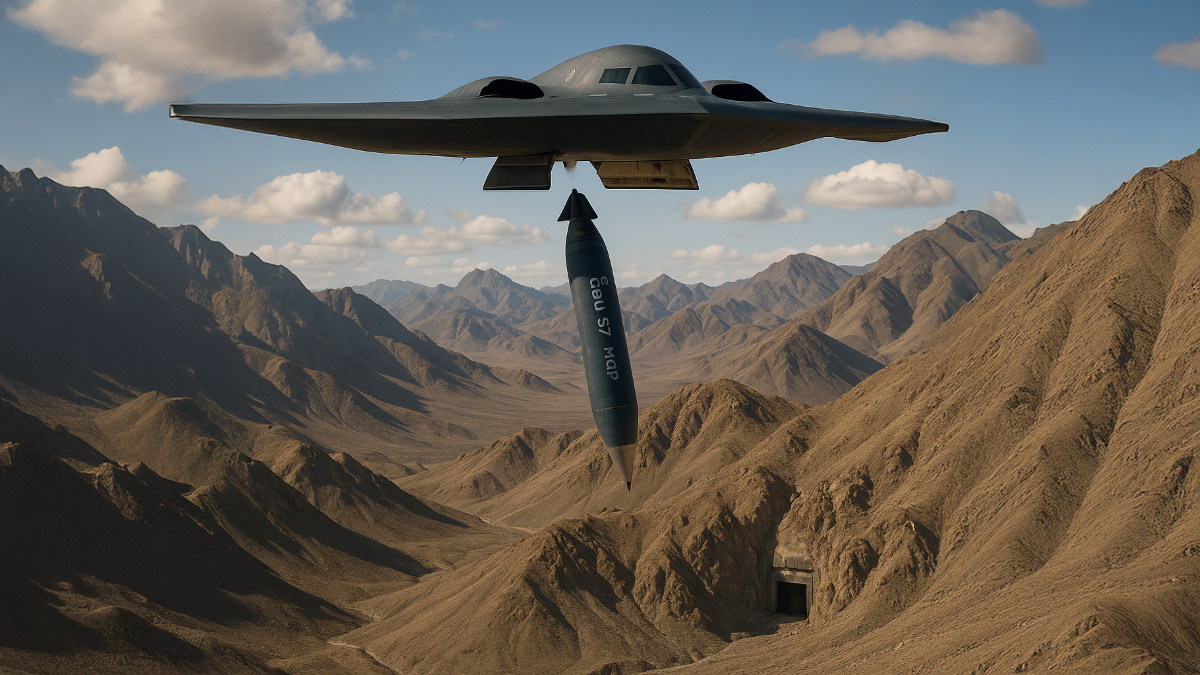
Bunker buster bombs are very heavy, hardened munitions designed to destroy fortified underground structures. They typically have extra-thick steel casings and high explosive charges so they can drill through earth, rock or reinforced concrete before detonating. Guided by GPS or laser systems for accuracy, bunker-busters rely on kinetic energy (mass × velocity) and time-delayed fuses to penetrate deep into the ground. For example, the U.S. GBU-57 “Massive Ordnance Penetrator” (MOP) is a 30,000‑lb (≈13,600 kg) GPS-guided bomb with a steel casing that can burrow up to about 61 meters underground .
Its warhead contains roughly 4,500 lb of high explosives, and it was developed specifically to reach fortified targets like Iran’s Fordow nuclear site . By contrast, the older GBU-28 is a 5,000‑lb (≈2,270 kg) laser-guided bomb used since the 1990s; it can penetrate on the order of 6 meters of reinforced concrete . Other U.S. bunker-busters include the GBU-43/B “MOAB” (21,600 lb, a surface-blast bomb used once in Afghanistan 2017) and the 2,000‑lb BLU-109 penetrator (≈1.2–1.8 m concrete) . Table 1 summarizes key types:
| Bomb Type | Weight | Penetration | Notable Use |
| GBU-28 (5,000 lb) | ~2,270 kg | ≈6 m reinforced concrete | Gulf War 1991 (Iraqi bunker) |
| GBU-57 MOP (30,000 lb) | ~13,600 kg | ≈61 m earth | First combat use June 2025 (Fordow, Iran) |
| GBU-43/B (MOAB) | 21,600 lb (9,800 kg) | Surface blast (no penetration) | Afghanistan 2017 (ISIS) |
| BLU-109/B (2,000 lb) | ~900 kg | ≈1.2–1.8 m reinforced concrete | Multiple conflicts (e.g. Iraq 2003) |
Bunker Buster Bombs work by concentrating explosive force deep underground. Some designs (like early GBU-28s) even had small rocket boosters to increase impact speed. In combat they are usually dropped from high altitude onto precise GPS or laser-designated coordinates. Upon impact, a short-delay fuse lets the bomb penetrate before exploding, maximizing damage to buried targets. The U.S. MOP (Massive Ordnance Penetrator) was fielded in the 2010s to reach the deepest tunnels and vaults, far exceeding older munitions . Notably, the GBU-57 MOP had its first known combat use during the June 2025 strikes on Iran’s Fordow nuclear site .
The B-2 Spirit Stealth Bomber
The B-2 Spirit is a long-range, low-observable (stealth) strategic bomber built by Northrop Grumman. It has a distinctive “flying wing” shape and is coated with radar-absorbent materials. Each aircraft cost about $2.1 billion and only 21 were built . A B-2 carries a crew of two pilots and can fly over 6,000 nautical miles (≈11,000 km) unrefueled . With aerial refueling it has near-global reach, enabling it to strike targets anywhere in the world from U.S. bases. Its internal bomb bays can hold up to 40,000 lb (≈18,000 kg) of ordnance while preserving the bomber’s stealthy profile.
Key specifications of the B-2 include:
- Crew: 2 pilots with advanced avionics and automation .
- Range: >6,000 nm (≈11,000 km) unrefueled .
- Speed: Subsonic (about Mach 0.85–0.95).
- Payload: Up to 40,000 lb of bombs and missiles . Internal bays can carry nuclear or conventional weapons.
- Stealth: Extremely low radar cross-section (“comparable to a small bird” ) via its shape and radar-absorbent materials.
- Armaments: Can carry precision-guided bombs (JDAMs, JSOW), cruise missiles (JASSM, JASSM-ER) and the GBU-57 MOP. It is the only U.S. aircraft currently able to carry the 30,000-lb MOP .
Because of its stealth, the B-2 can penetrate advanced air defenses undetected and deliver precision strikes on heavily defended or fortified targets. For example, the USAF modified the B-2 to carry two 14-ton MOP bombs . The bomber is also nuclear-capable (able to carry B61 and B83 thermonuclear bombs) and serves as a key part of the U.S. nuclear deterrent.
Historically, the B-2 has been used sparingly in combat. Its first combat use was in the 1999 Kosovo War, when it dropped JDAM bombs on Serb targets . It later saw action in Afghanistan (2001), Iraq (2003) and Libya (2011), typically dropping precision guided bombs against high-value or hidden targets. (For instance, B-2s flew from Missouri to strike Taliban and al-Qaeda positions in Afghanistan in late 2001.) More recently, in 2017 B-2s were used against Islamic State militants in Libya, reportedly killing dozens of fighters . Each deployment demonstrated the bomber’s ability to strike without warning – e.g. one flight in 2003 flew from Missouri, refueled dozens of times, and struck targets near Baghdad.
The B-2 remains an elite, high-demand asset. Its nuclear-capable design and long range give it a strategic role in U.S. defense. Due to its high cost and limited numbers, U.S. leaders use it only in critical situations. As Secretary of Defense Lloyd Austin noted after a 2025 strike on Yemen, the B-2 “targets facilities that our adversaries seek to keep out of reach… no matter how deeply buried underground” . In short, the B-2 plus bunker-buster bombs provide the U.S. with a uniquely potent capability to hit the world’s most protected targets.
Historical Uses of Bunker Buster Bombs and the B-2
Over the past three decades, bunker buster bombs have played key roles in several wars. In the 1991 Gulf War, the U.S. Army rushed the GBU-28 into service (completed in under three weeks) to punch through Iraqi bunkers and command centers . That bomb successfully demolished an underground Iraqi military bunker at Alam al-Muthanna. Bunker-busters (GBU-28s, BLU-109s and later JDAM-equipped penetrators) were also used throughout the Afghanistan and Iraq wars to collapse cave complexes and fortified compounds. Even extremely large conventional bombs have been used – for example the 21,600-lb GBU-43 MOAB was dropped in 2017 on ISIS tunnels in Afghanistan to collapse a vast network of caves. Other countries have their versions: Russia has the 1,500-kg FAB-1500 penetration bomb, and Israel and NATO allies use similar munitions.
The B-2 stealth bomber’s history of use is shorter but dramatic. Its stealth was first proven in Kosovo, where it evaded Yugoslav air defenses. In 2001–03 it flew some of the longest combat missions in history into Afghanistan and Iraq. In Libya (2011) it again struck hidden targets (such as air defenses) to pave the way for allied operations. A 2025 strike on Yemen’s Houthi rebels showed the B-2 could still project power: two B-2s flew 15 hours from Missouri to hit underground bunkers in Yemen, marking its first combat use in years . Altogether, the B-2 has dropped conventional bombs in multiple conflicts – highlighting its role as a strategic hammer for the U.S., especially against targets that lighter aircraft cannot reach.
Both Bunker Buster Bombs and the B-2 form part of a strategic toolkit for targeting deep underground facilities. The combination of GPS guidance, massive weight and precision allows bunker-busters to collapse nuclear sites or command bunkers. The B-2’s stealth lets it deliver those weapons with surprise. As one defense analyst noted, Iran’s Fordow facility “sits between 80 m and 90 m below the mountain peak,” making it practically invulnerable to ordinary bombs. Only the GBU-57, carried by a B-2, had a chance to damage it .
June 2025: U.S. Airstrikes on Iran’s Nuclear Sites with Bunker Buster Bombs
On June 21–22, 2025, the United States conducted airstrikes on Iran’s nuclear program – a major escalation after Israel had struck targets in Iran. In a televised address, U.S. President Donald Trump announced that “U.S. forces struck Iran’s three main nuclear sites” – Natanz, Isfahan and Fordow – calling the attack a “spectacular military success” and saying Iran’s key enrichment facilities had been “completely and totally obliterated” . According to U.S. officials and media reports, B-2 stealth bombers played a central role. A U.S. military source told Reuters, on background, that B-2s carried out strikes on Fordow with massive bunker-buster bombs . The president later posted that “a full payload of BOMBS was dropped on the primary site, Fordow” and that “Fordow is gone” .
Multiple sources confirm the details: President Trump said six bunker-buster bombs were dropped on Fordow, while about 30 U.S. submarine-launched Tomahawk cruise missiles hit the Natanz and Isfahan sites . He and Pentagon officials noted that all U.S. aircraft safely returned to base. An anonymous U.S. official told Reuters that B-2 bombers were involved in the strikes . Israeli officials had earlier requested the U.S. use GBU-57 MOP bombs to destroy the mountain-buried Fordow site, and indeed bunker-buster bombs were used on Fordow . In fact, reports indicate this was the first combat use of the 30,000-lb GBU-57 weapon . (Israel’s earlier strikes had not penetrated Fordow’s vault.)
The sequence was roughly as follows:
- Who: The strikes were launched by U.S. forces at the direction of President Trump, in coordination with Israel. U.S. B-2 bombers (based at Whiteman AFB, Missouri) flew a long-range mission to Iran’s airspace. U.S. Navy submarines in the region fired Tomahawks. Overall, this marked the first direct U.S. involvement in what had been an Israel-Iran conflict.
- Targets: The main targets were Iran’s nuclear enrichment sites. Fordow (near Qom) and Natanz (Isfahan Province) produce enriched uranium, and both are protected underground. Isfahan hosts a heavy water reactor facility. Trump specifically named Fordow as “the primary site” and confirmed the others were hit .
- Weapons: The U.S. used a combination of weapons. At Fordow, bunker-buster bombs (GBU-57 MOP) were reportedly dropped from B-2s – at least six such bombs on Fordow alone . (Tomahawks cannot reach Fordow’s depth, so the B-2/MOP was chosen.) At Natanz and Isfahan, around 30 Tomahawks attacked infrastructure. All weapons were conventional (non-nuclear). U.S. officials emphasized the precision of the strikes.
- First Use of MOP: U.S. and Israeli planners consider Fordow the hardest target on Earth. The GBU-57 MOP’s first combat deployment took place in this mission . U.S. Secretary of Defense Lloyd Austin said the strikes demonstrated the ability to hit “no matter how deeply buried” (alluding to Fordow) .
After the strikes, Iran’s official media acknowledged damage. One Iranian statement claimed no “serious damage” and no radiation release , while another lawmaker said the facility was evacuated and its materials removed prior to the attack. The U.S. indicated it aimed to degrade Iran’s nuclear capability without forcing a regime change or causing major collateral harm. President Trump claimed all planes were “now outside Iran air space” , suggesting no U.S. losses.
Bunker Buster Bombs Implications and Reactions
The U.S. use of the B-2 and bunker-busters against Iran’s nuclear sites drew immediate global attention. Officials noted this as a major escalation. United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres warned of a “dangerous escalation” that threatens international peace . Iran’s leaders vowed consequences: Iran’s foreign minister called the U.S. strikes “outrageous” and said Tehran “reserves all options” to retaliate . Major regional players are scrambling; for example, Israel closed its airspace after the U.S. attack and allies urged calm.
Economically, markets reacted to war fears. Analysts expected a “knee-jerk” spike in oil prices and a flight to safe-haven assets . Indeed, by June 22 oil futures jumped on the news of the strikes. Financial commentators warned that higher oil and risk aversion could slow the global economy. Airlines were quickly re-routing flights to avoid Middle East airspace, leading to longer routes and higher costs .
Militarily, the strikes demonstrated U.S. capabilities. The B-2/MOP combination was shown to work in practice, potentially undermining the security of any deeply buried site. Some analysts noted this could deter Iran’s nuclear ambitions, but also could accelerate them if Iran races to rebuild its capacity. The Middle East region is now at a heightened risk of wider conflict. U.S. leaders face pressure over the legality and wisdom of the strike: some U.S. lawmakers noted that, as required by law, Congress was not consulted before the attack . Domestically in the U.S., the strikes were supported by some politicians as decisive action, while others – including some allied Republicans and Democrats – questioned the authority and potential consequences.
In summary, bunker-buster bombs and the B-2 Spirit have long been critical tools for precision strikes on hardened targets. In June 2025, they were used together in a real-world test when U.S. forces hit Iran’s fortified nuclear facilities. Eyewitness reports from Reuters and AP confirm that B-2s dropped heavy bunker-busters on Fordow, while Tomahawks hit Natanz and Isfahan . The operation’s aftermath – from Middle East tensions to global markets – is still unfolding, illustrating how these advanced weapons have profound strategic implications.
Sources: Official military sources and leading news agencies report details of the weapons and missions. Technical specifications are drawn from U.S. Air Force and industry data . Information on recent strikes comes from Reuters and AP dispatches on June 21–22, 2025 , and from government statements (e.g. President Trump’s address) cited therein. All facts are corroborated by multiple defense and news outlets.