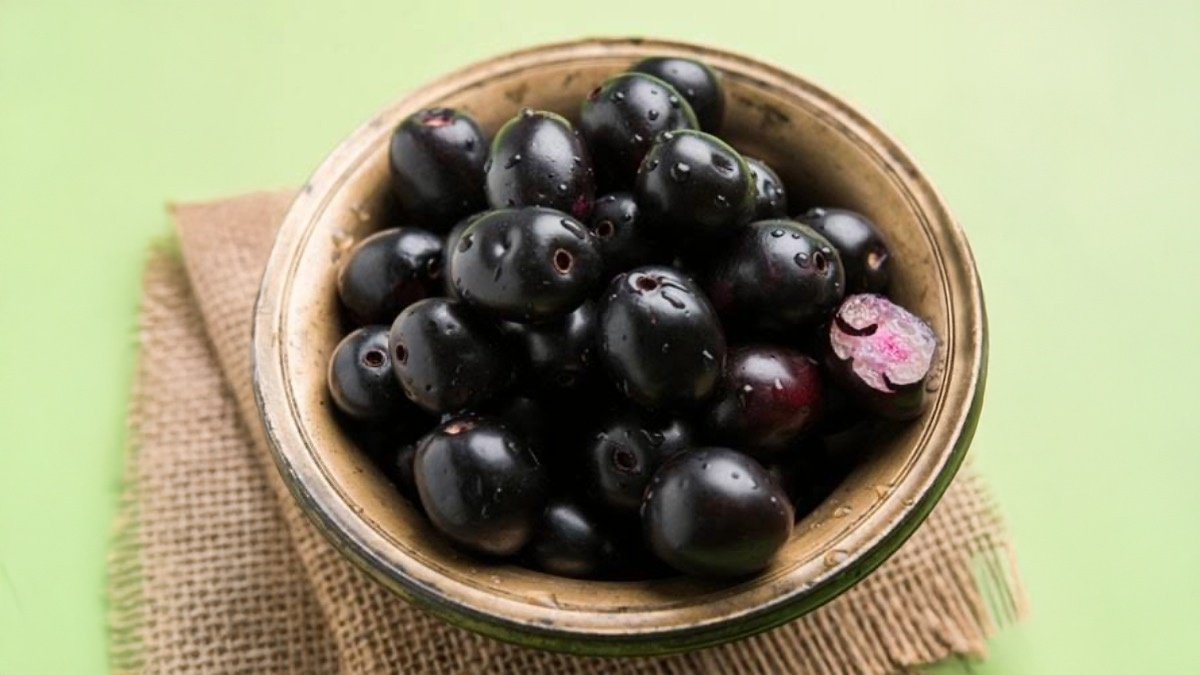
Jamun fruit benefits: Jamun, also known as Indian blackberry or Java plum, is a juicy, dark purple fruit that’s loved not only for its tangy-sweet flavor but also for its remarkable health benefits. Native to the Indian subcontinent, Jamun is widely available during the summer and monsoon seasons. Rich in nutrients and bioactive compounds, it has been used in Ayurvedic and traditional medicine for centuries. But while Jamun is a superfood for many, it’s not ideal for everyone.
In this article, we’ll explore the Jamun Fruit Benefits, who should include it in their diet, and who should avoid it for health reasons.
Nutritional Value of Jamun
Jamun is low in calories and packed with nutrients. A 100-gram serving contains:
- Calories: 60–75 kcal
- Carbohydrates: 14 g
- Fiber: 0.6 g
- Vitamin C: 18 mg
- Iron: 1–2 mg
- Calcium: 15–20 mg
- Magnesium, Potassium, and B Vitamins: Trace amounts
Additionally, it is rich in antioxidants such as anthocyanins, flavonoids, and polyphenols that offer multiple health benefits.
Top Health Benefits of Jamun
1. Regulates Blood Sugar Levels
Jamun Fruit Benefits, Jamun is especially beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes. The fruit contains jamboline and jambosine, compounds that help slow down the conversion of starch into sugar. The seed powder of Jamun is also widely used as a natural remedy for blood sugar control.
2. Boosts Digestion
Jamun helps improve digestion due to its high fiber content and astringent properties. It relieves constipation, bloating, and flatulence, making it ideal for those with digestive issues.
3. Strengthens Immunity
The presence of vitamin C and antioxidants helps strengthen the immune system. Jamun is effective in fighting infections, reducing inflammation, and supporting overall health.
4. Improves Skin Health
Jamun has antibacterial and antioxidant properties that help purify the blood, leading to healthier skin. It may help reduce acne, pimples, and skin blemishes when consumed regularly.
5. Good for Oral Health
Chewing Jamun leaves or using Jamun bark powder can help prevent gum bleeding and bad breath. Its antibacterial properties make it effective in maintaining oral hygiene.
6. Supports Heart Health
Rich in potassium, Jamun helps regulate blood pressure and supports cardiovascular health. The antioxidants in the fruit also prevent oxidative damage to the heart and blood vessels.
7. Helps in Weight Management
Jamun is low in calories and has a high water content, making it a good snack for weight watchers. It keeps you full for longer and helps control cravings.
Who Should Eat Jamun?
Jamun is highly beneficial for the following groups.
People with Diabetes
The natural compounds in Jamun help lower blood sugar levels. Consuming the fruit or its seed powder can be a part of a diabetic-friendly diet (under medical supervision).
Individuals with Digestive Issues
Those suffering from indigestion, acidity, or constipation can benefit greatly from Jamun due to its digestive-enhancing properties.
People with Skin Problems
Jamun helps in purifying the blood and can be effective for people suffering from acne, pimples, and oily skin.
Heart Patients
Its potassium content supports heart health and helps regulate blood pressure naturally.
Those with Weak Immunity
With antioxidants and vitamin C, Jamun can strengthen the immune response and help fight seasonal infections.
Who Should Avoid Jamun?
Although Jamun is safe for most people, some should avoid or limit its intake:
People with Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
Since Jamun lowers blood sugar levels, people who already have low sugar levels should consume it cautiously to prevent hypoglycemia.
Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women (in Excess)
Moderate consumption is safe, but overconsumption might lead to acidity or affect sugar levels. Always consult a doctor before including Jamun or seed powder in large amounts during pregnancy.
Individuals with Sore Throat or Cold
Jamun is slightly acidic in nature. Eating it during a sore throat or cold may worsen the symptoms, especially if consumed chilled.
People Prone to Acidity
Though Jamun helps digestion, excessive intake can trigger acidity or gastric discomfort in sensitive individuals.
Post-Surgery Patients
Jamun can interfere with blood sugar levels. Patients recovering from surgery should avoid Jamun before and after surgery, especially if on blood-sugar controlling medications.
How to Consume Jamun
- Fresh Fruit: Washed and eaten as a mid-day snack.
- Juice: With a pinch of black salt and cumin for digestion.
- Seed Powder: Used in traditional medicine for diabetes management.
- Jamun Vinegar (Sirka): Consumed in small amounts before meals to boost digestion.
Important Tips
- Avoid drinking milk immediately after eating Jamun.
- Do not eat Jamun on an empty stomach.
- Always wash the fruit thoroughly before consumption to remove any pesticide residue.
- Don’t overconsume—4 to 8 pieces per day is usually enough for an adult.
Jamun fruit benefits, Jamun is a nutritional powerhouse with multiple health benefits, particularly for diabetics and those looking to boost digestion and immunity.Jamun Fruit Benefits However, like all natural remedies, it should be consumed in moderation and with awareness of any underlying health conditions. Consulting a healthcare professional before starting any new dietary inclusion is always a wise decision—especially for individuals with specific medical needs.